Divine Tips About How Do You Plot A Straight Line Graph Data Horizontal To Vertical In Excel
How to plot a straight line graph.
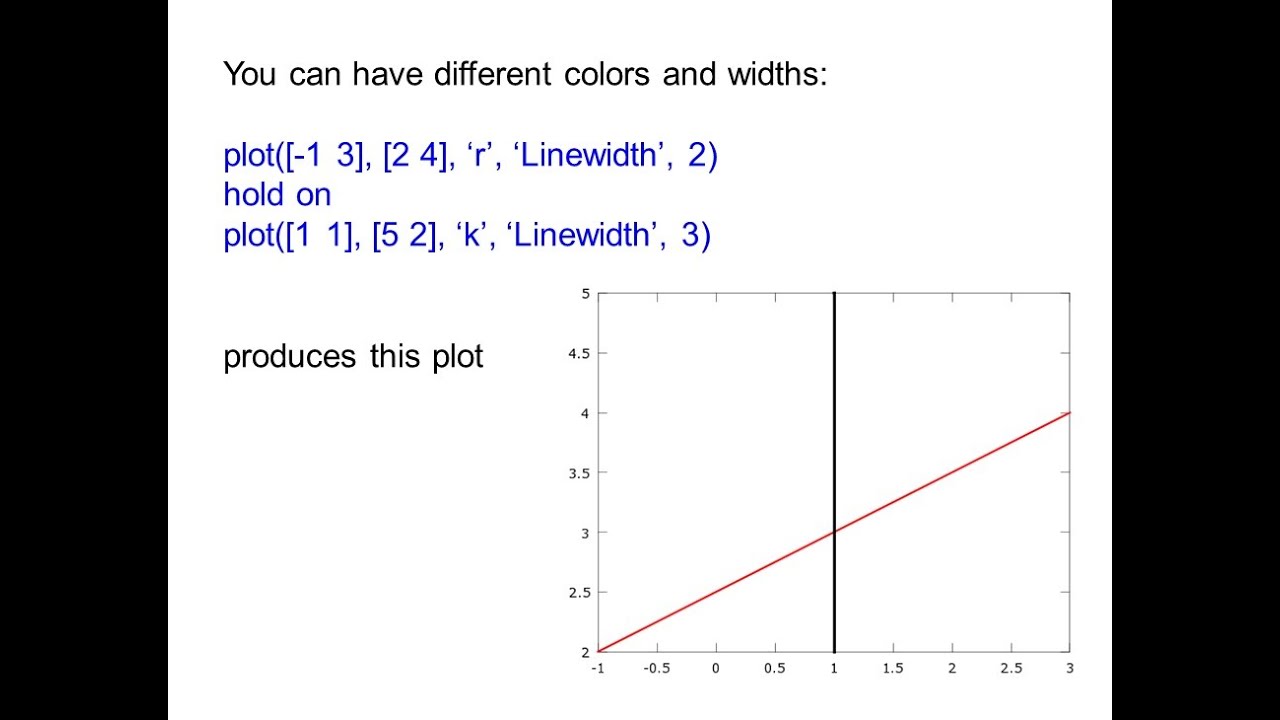
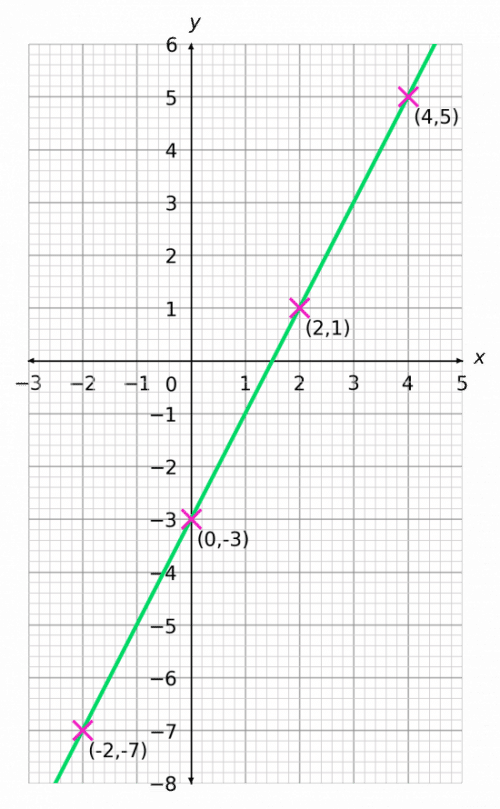
How do you plot a straight line graph. Graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more. Plot the points on a rectangular coordinate system. Draw the line through the points.
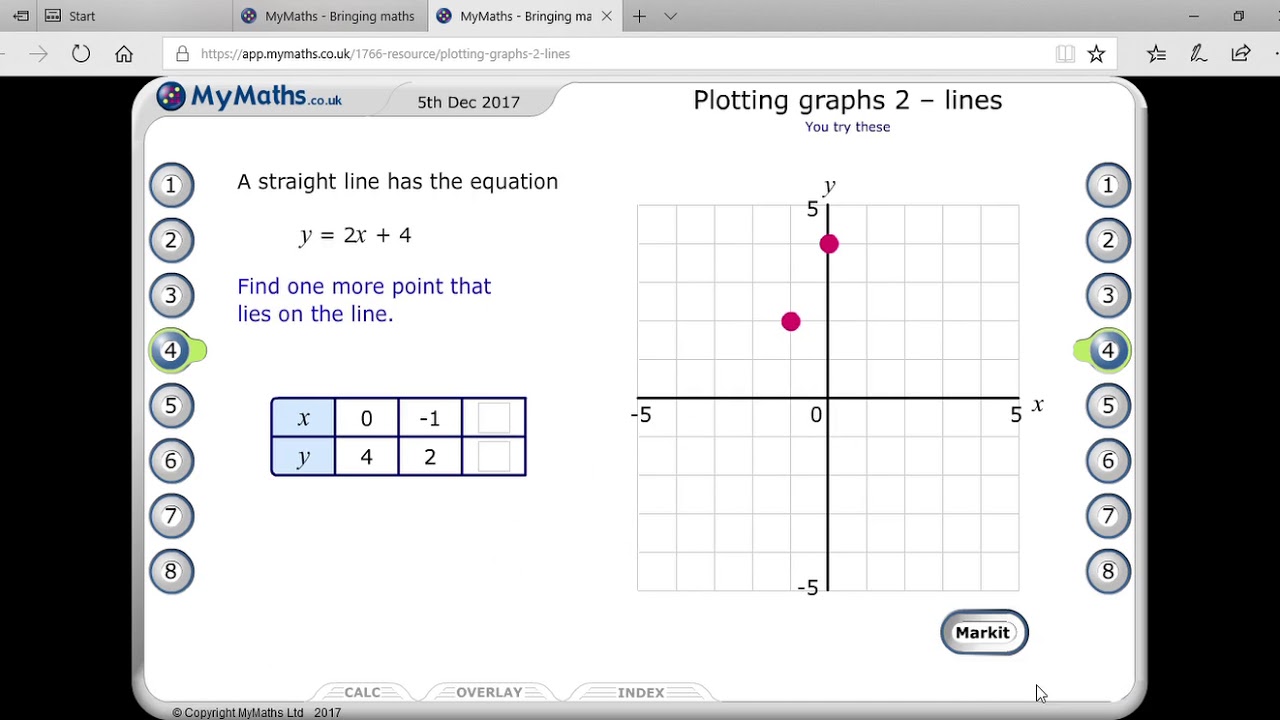
How do we find m and b? Learn how to read x and y coordinates from a graph in this bbc bitesize maths ks3 guide. Check that the points line up.
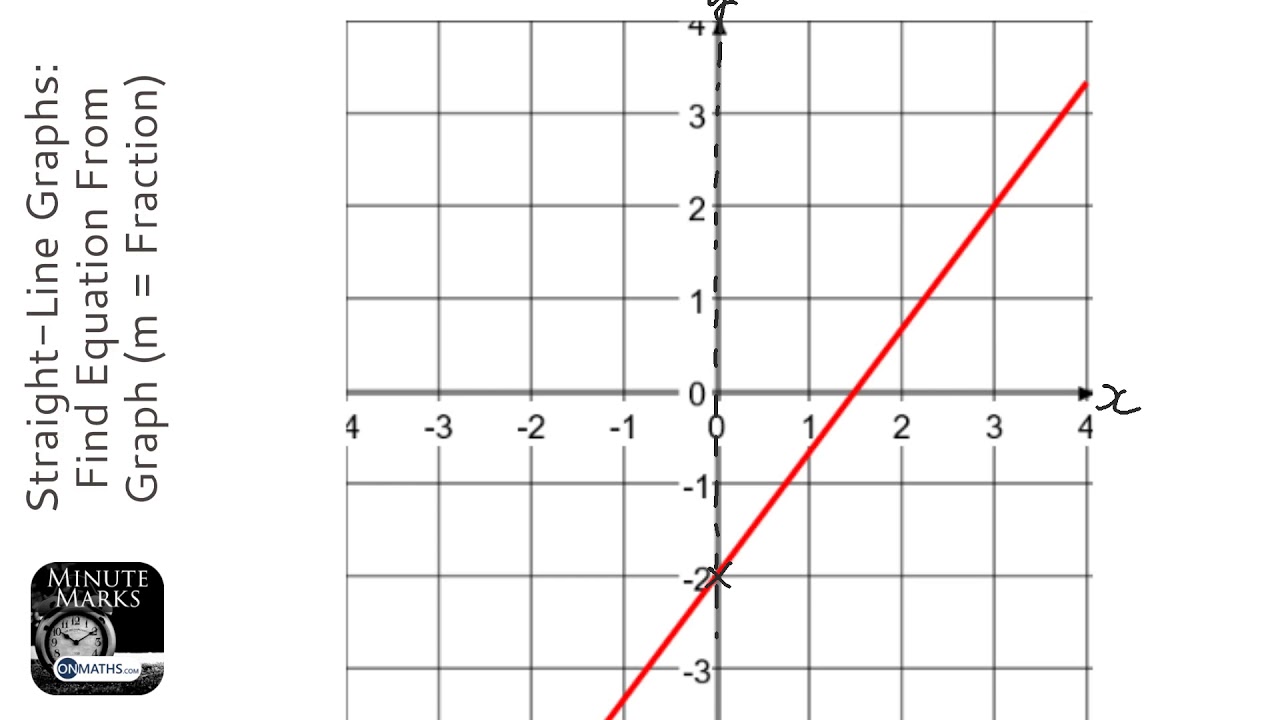
Just enter the two points below, the calculation is done live. Y = mx + b. Use the power of algebra to understand and interpret points and lines (something we typically do in geometry).
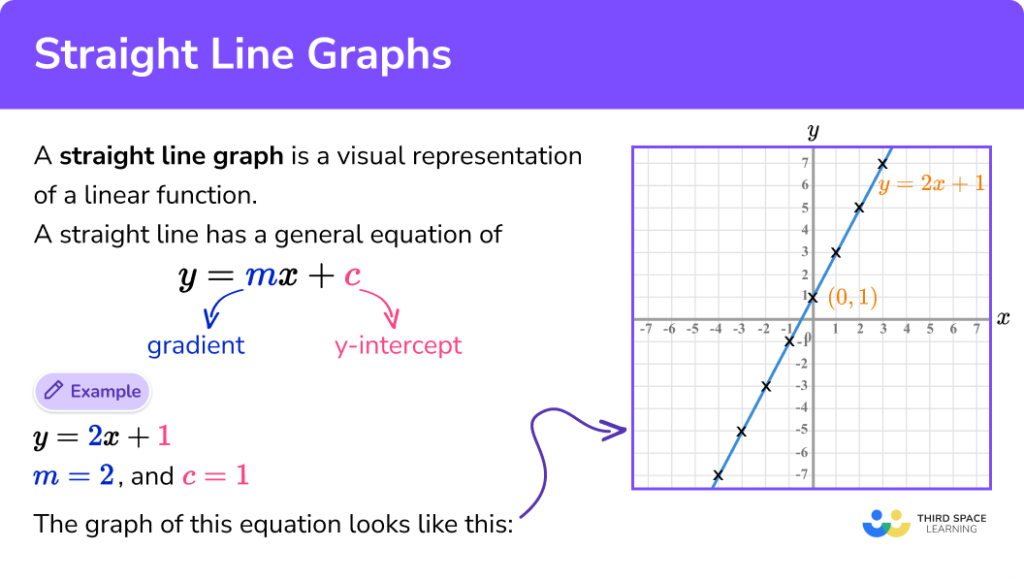
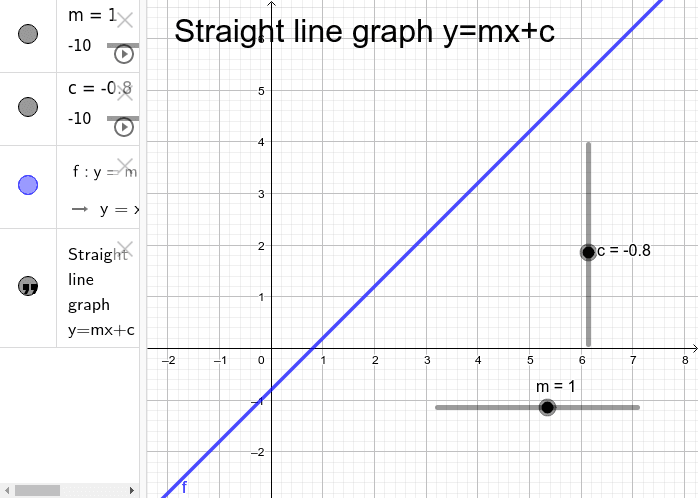
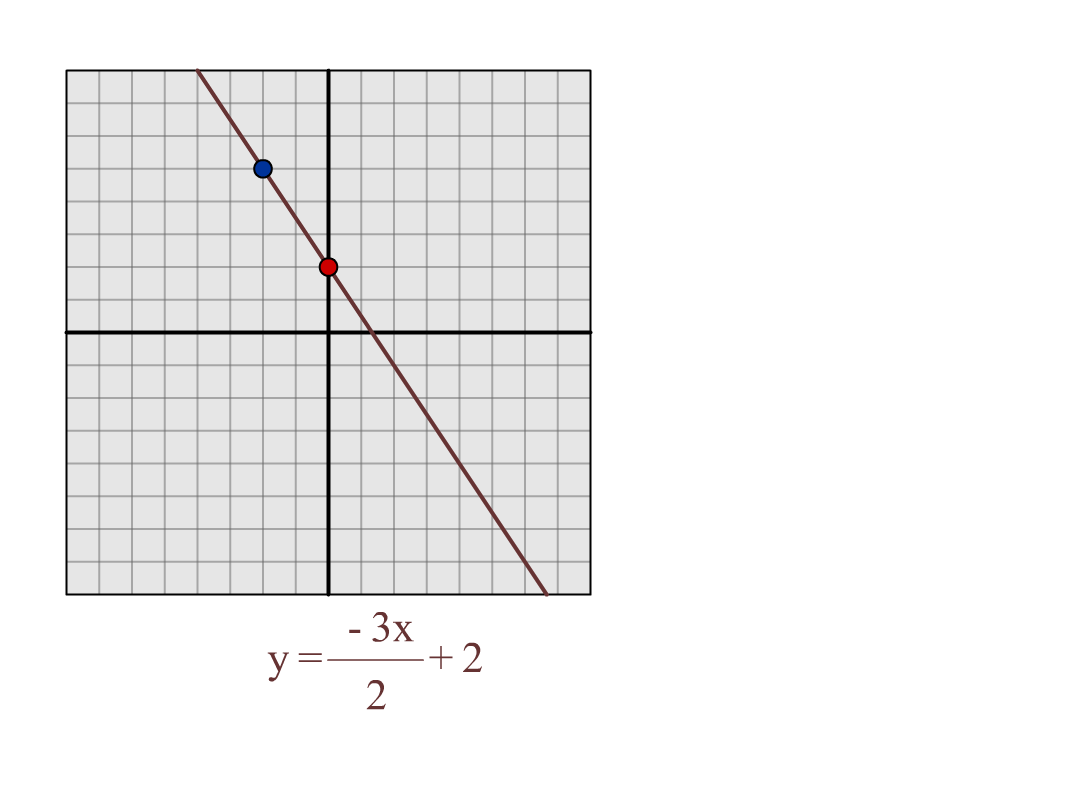
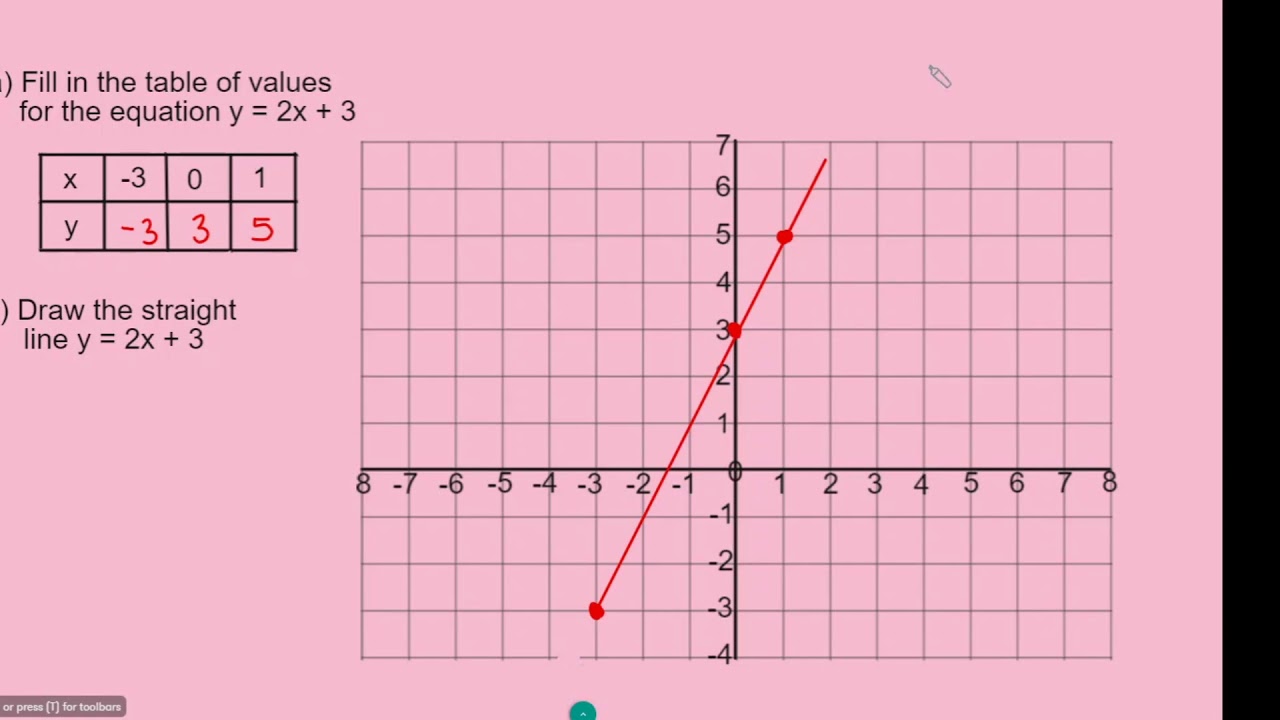
Constructing a table of values. Move the m and b slider bars to explore the properties of a straight line graph. The equation of a straight line is usually written this way:
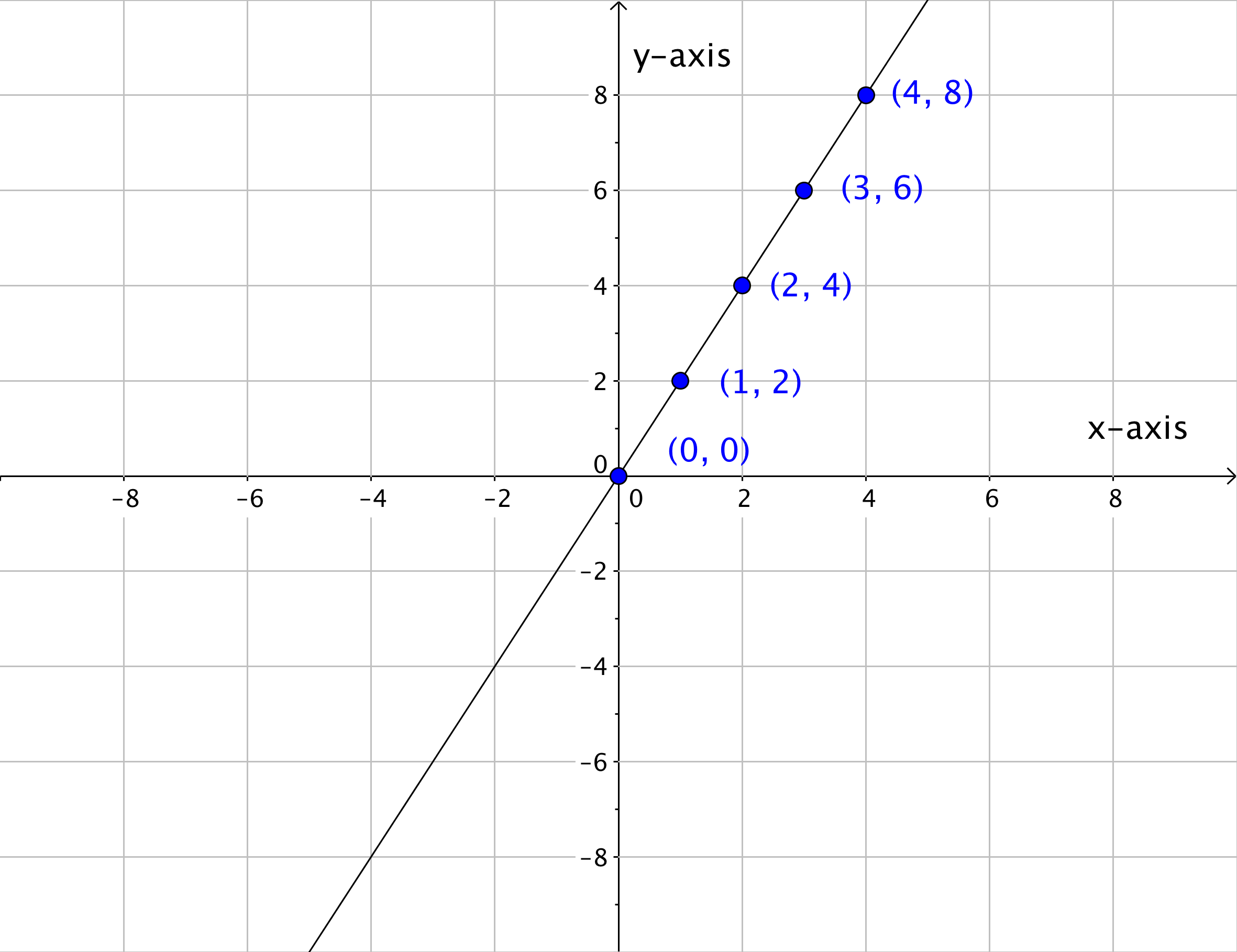
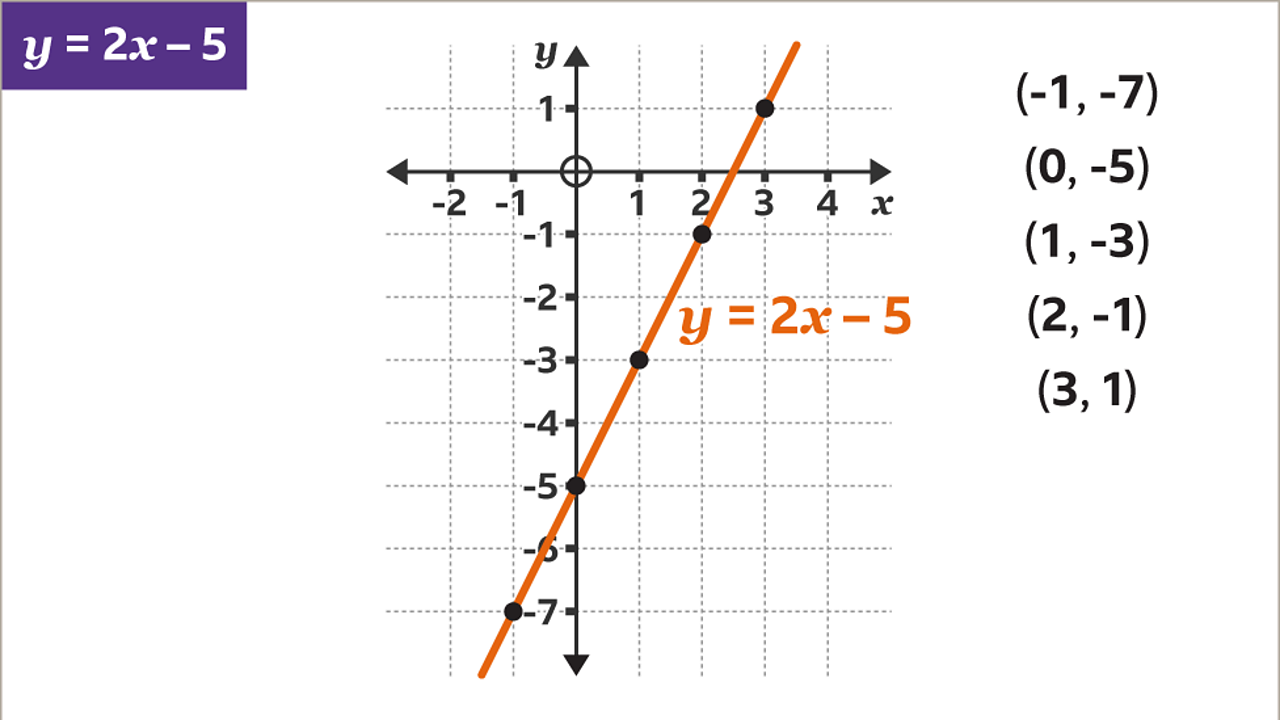
Y = how far up. We can use a table of values to show the number pairs: We can instead find pairs of x and y values that make the left side equal the right side.
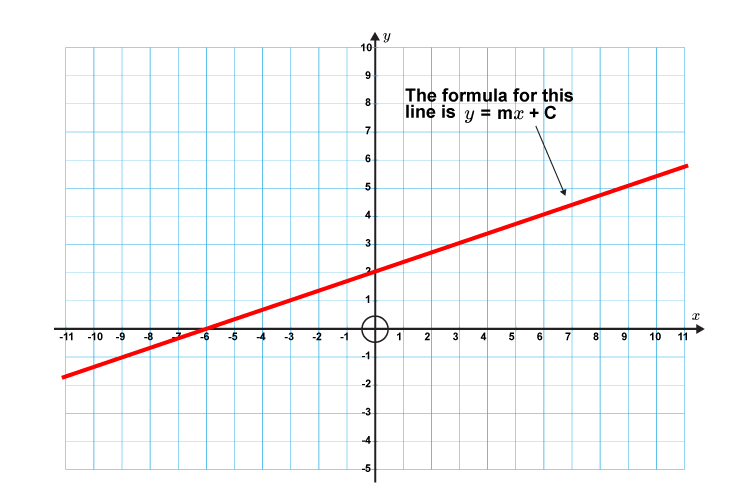
The effect of changes in m. (or y = mx + c in the uk see below) what does it stand for? So how do you make a line graph?
Either way, make sure the line goes through as many points as possible with equal numbers of. And we have our little khan academy graphing widget right over here, where we just have to find two points on. What we need to do is to select some values of x and then evaluate those values in the given equation to get the corresponding values of y.
When we have an equation with two different unknowns, like y = 2x + 1, we cannot solve the equation. Join each data point to the next, using straight lines. Just follow these steps below to find out.
Line charts are used to display trends over time. If you know two points, and want to know the y=mx+b formula (see equation of a straight line ), here is the tool for you. Draw a straight line through all the plotted coordinates across the whole plotting area.
The effect of changes in b. Use a line chart if you have text labels, dates or a few numeric labels on the horizontal axis. M = slope or gradient (how steep the line is) b = value of y when x=0.