Nice Info About What Is A Dual Axis Chart Used For Gridlines Js
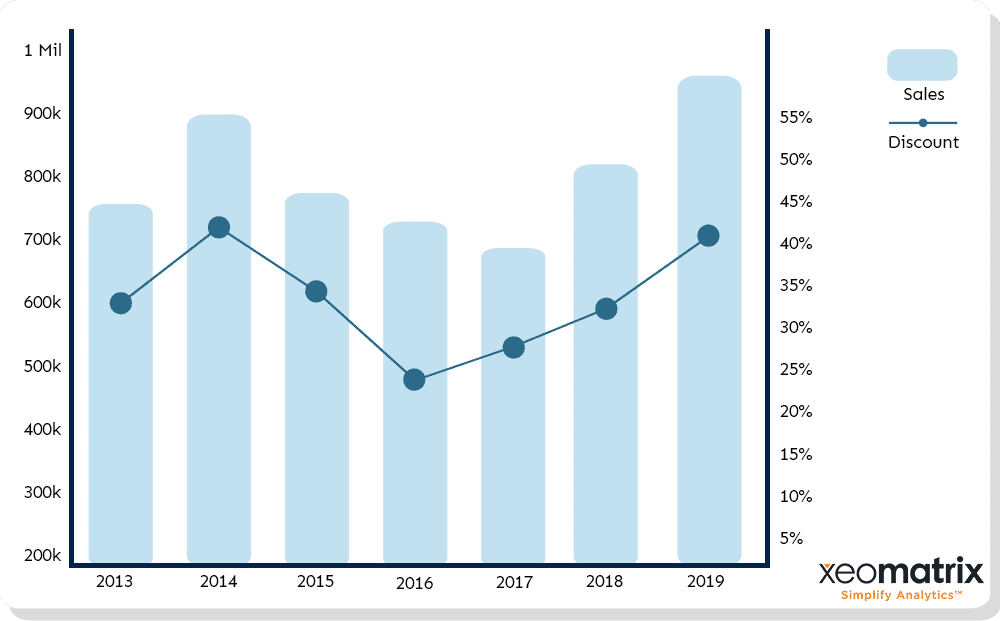
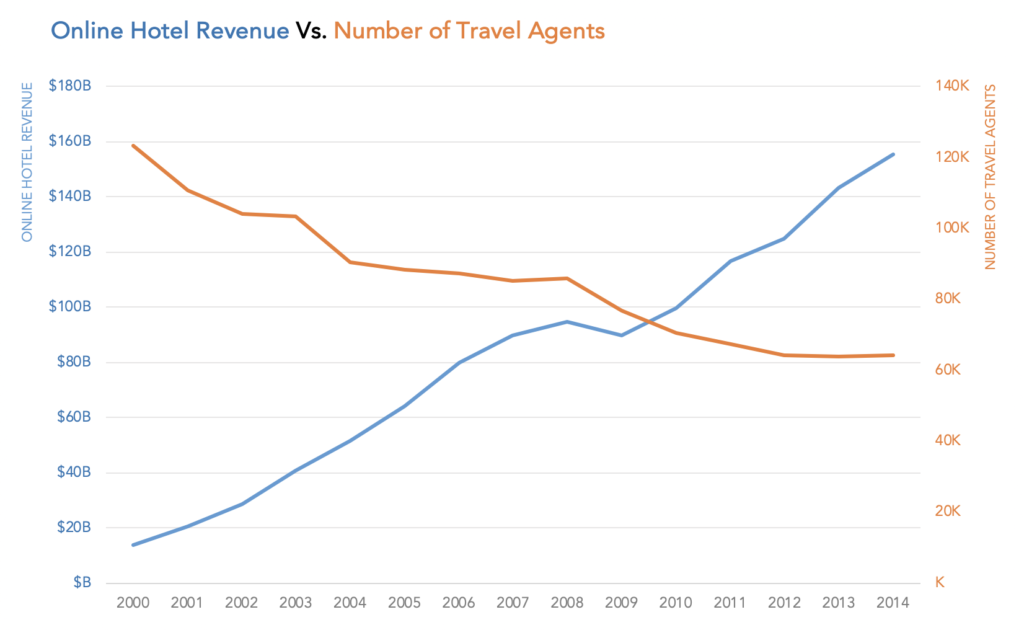
A dual axis chart also known as multiple axes chart, employs two axes to clearly depict the connections between two variables of varying magnitudes and scales of measurement.
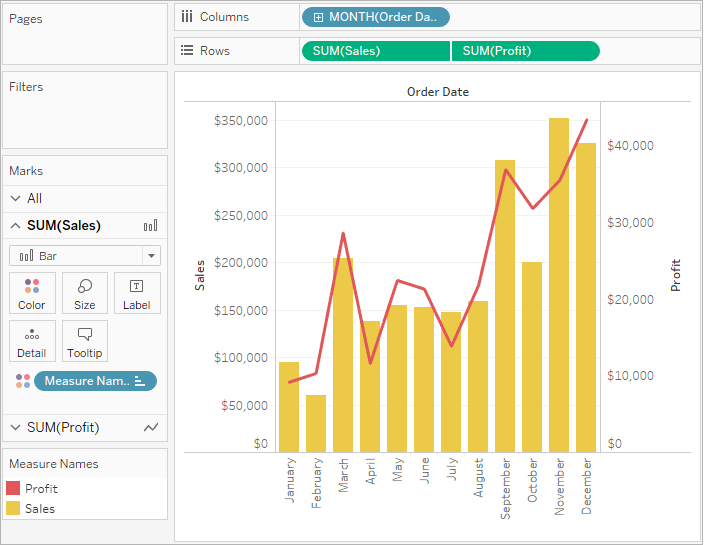
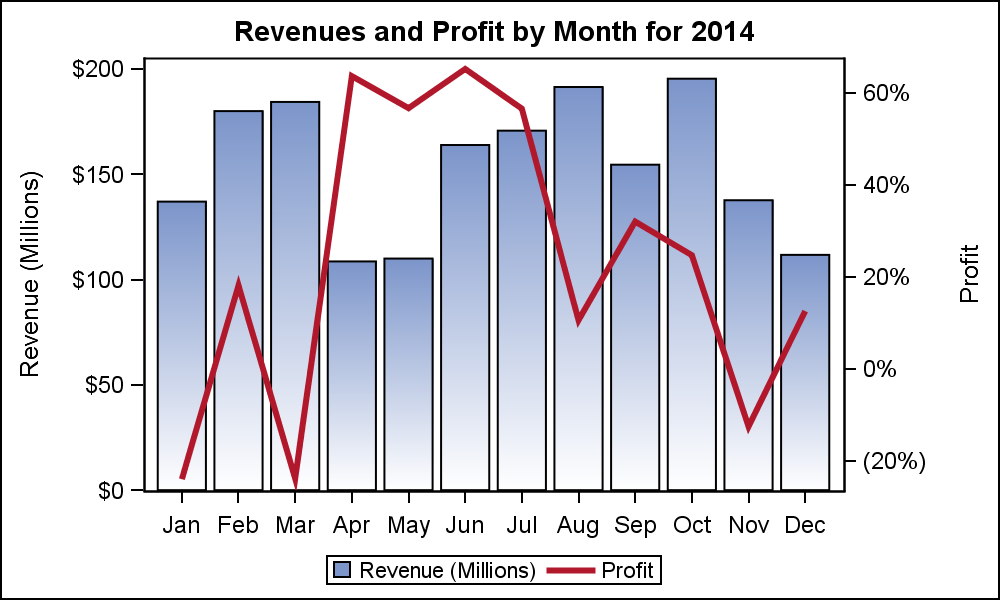
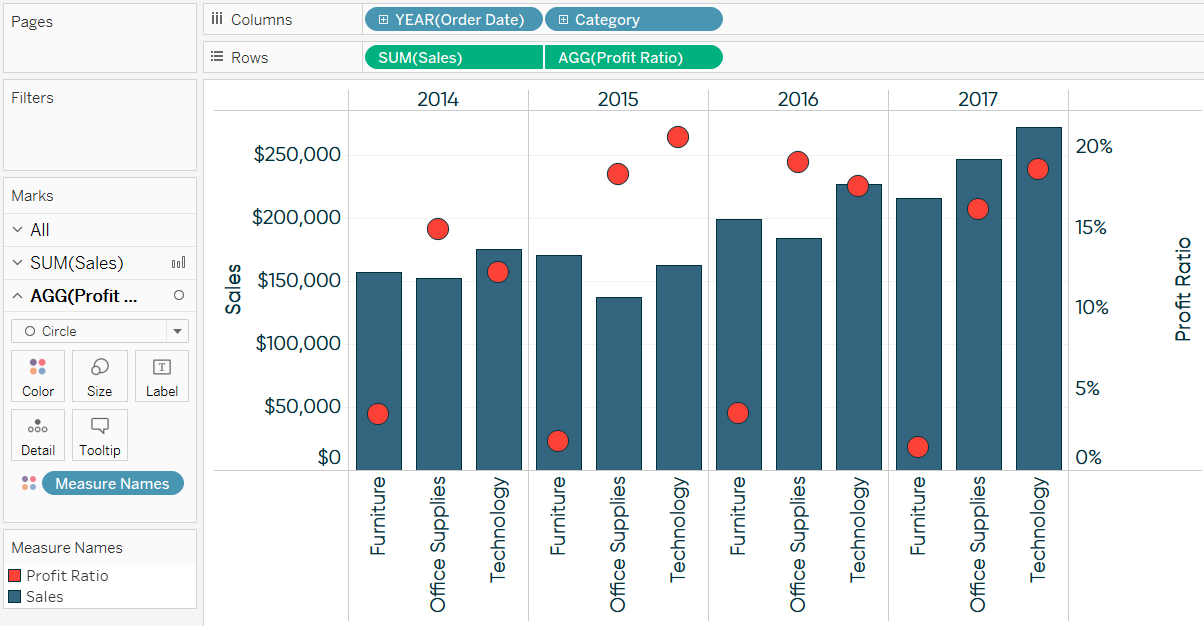
What is a dual axis chart used for. A double line graph uses two axes to illustrate the relationships between two variables with different magnitudes and scales of measurement. Now we have our dual axis chart and synchronized our axis for our quick analysis. A dual axis chart (also called a multiple axes chart) uses two axes to easily illustrate the relationships between two variables with different magnitudes and scales of.
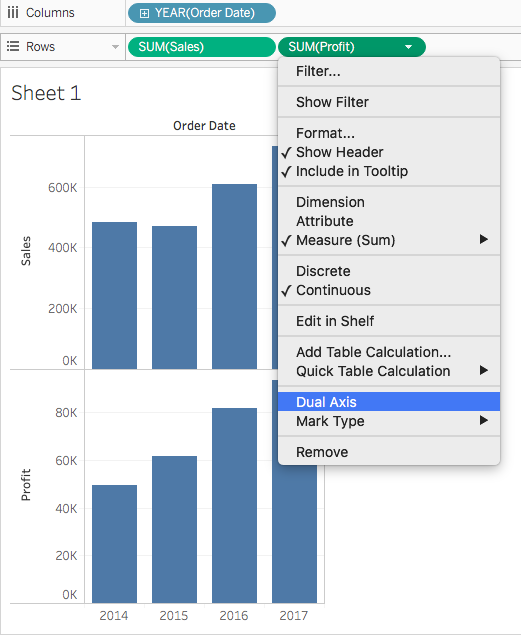
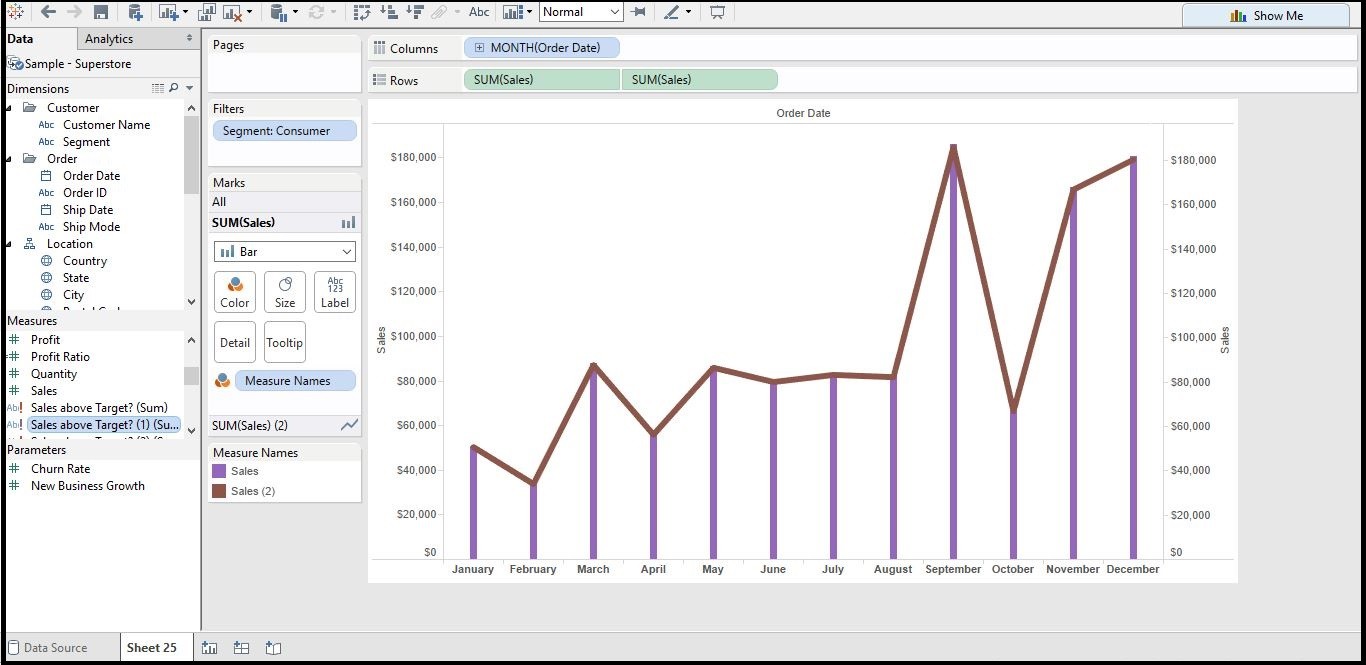
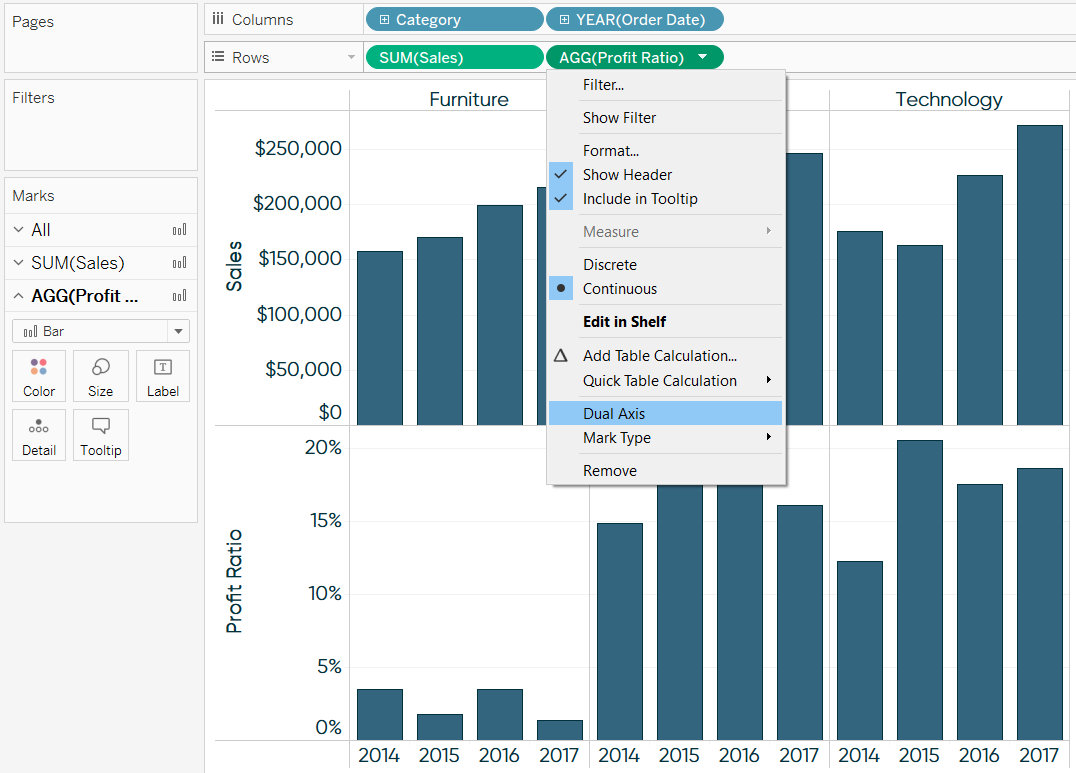
Following pointers will be covered in this article, how to build tableau dual. This video introduces the dual axis chart and shows how you can have two mark types on the same. Dual axis in tableau combines two measures on a single chart with separate axes.
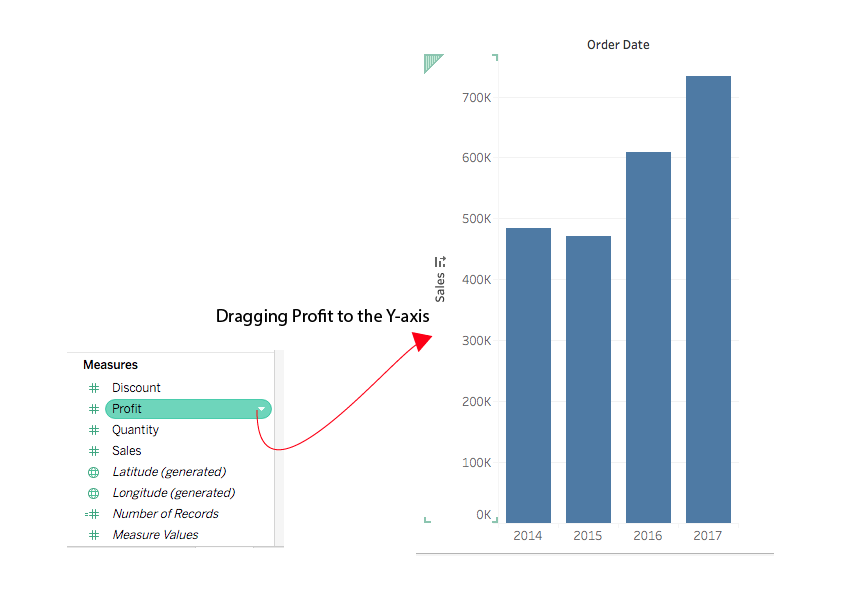
The purpose of this type of visualization is to show how one set of data changes. (1) their traditional use (2) a method for making your end. In order to show a line for each gender's change in life expectancy over time on the same set of axes, you'll need to make a dual axis chart.
Why do we use dual axis charts? A dual axis chart lets you combine measures that differ in scale and units. We use dual axis charts.
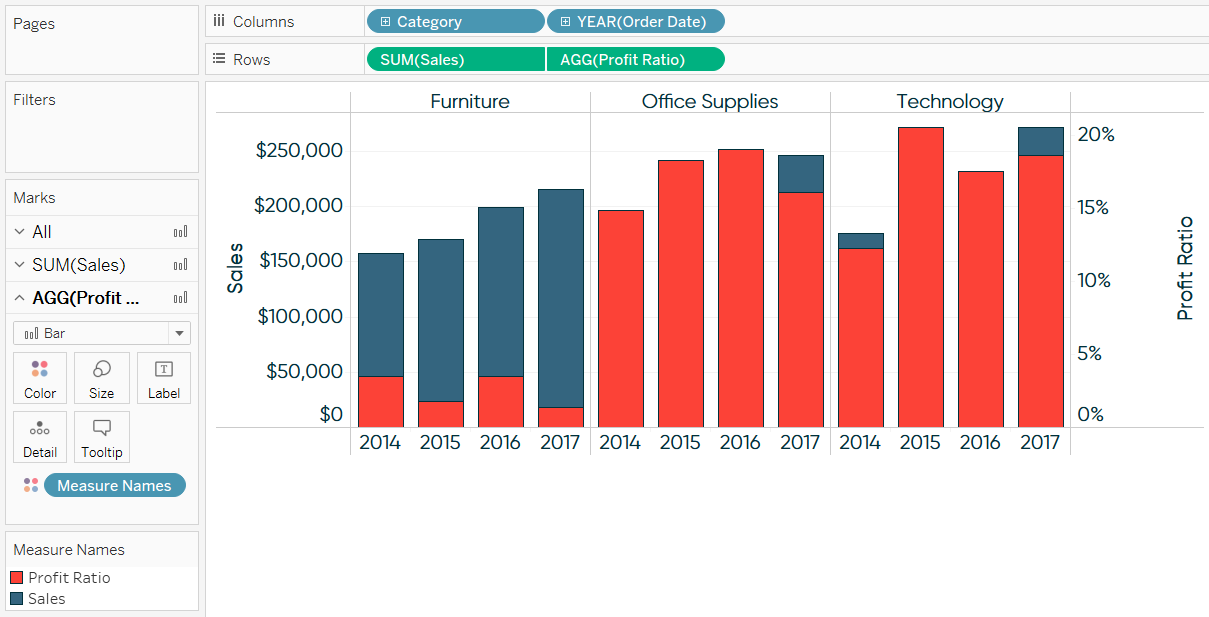
This article will introduce you to various ways to use dual axis charts in tableau. Maybe you want to take this further and add a few. Dual axis charts plot two data series on the same chart using a secondary axis.
By combining these measures in a single. It facilitates comparison between measures with different scales or units. A dual axis chart creates two independent axes (which you can synchronise) that you can plot two separate measures on in the same chart.
Whether comparing bar sizes, slices of a pie or the varying height of a line, the main advantage of data visualization dashboards. This has one big positive that it. What are dual axis charts?
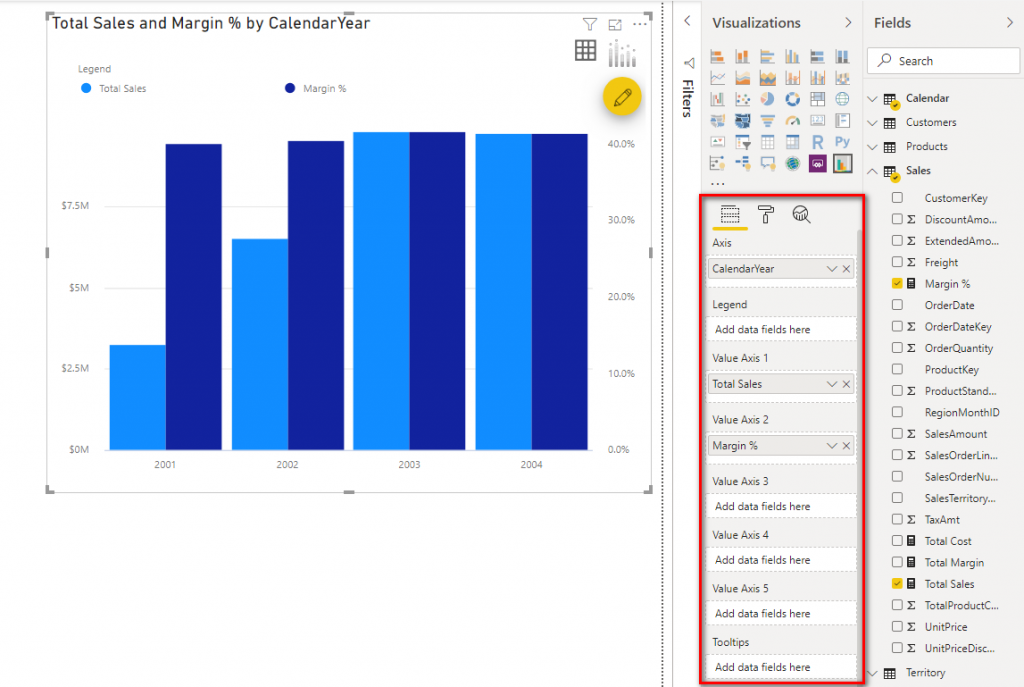
Using a dual axis chart in power bi provides a robust way to compare and analyze two measures with different units or scales.